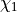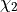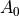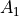Input Cards by Function¶
Normal Program Managment Commands¶
c
Comment - ignored.
name
parameters
c[ COMMENT ]
c the parameter settings below make the run more smoothComment Card.
- COMMENT
is an arbitrary alphanumeric string that is ignored by the code. Note that it must be separated from the c by at least one space.
Other entry:
Useful Input Cards
#
Same as c.
name
parameters
#[ COMMENT ]
d
Make a restart dump.
name
parameters
d[ FILENAME ]
d s12g d #mydumpFILENAME
name of file to which to write a current restart dump
If FILENAME is not provided, the restart dump is written to file name NAMEPROBz where NAMEPROB is the current problem name.
If FILENAME starts with # then the dump is written to file name NAMEPROB#FILENAME.
If FILENAME is # then the dump is written to file name NAMEPROB#NCYC where NCYC is ncyc (q 4).
Changed In Version >16.0.0: Added #FILENAME option.
Changed In Version 17.1.7: Added blank # option.
?
Evaluate expression.
name
parameters
?EXPRESSION
? p 2 * 2. ? dn(3) * rn(3)**3EXPRESSION
legal expression that can be evaluated in command files
New In Version 17.0.12.
@
Evaluate logical expression.
name
parameters
@EXPRESSION
@ p 2 > 2. @ dn(3) * rn(3)**3 >= dn(4) * rn(4)**3EXPRESSION
legal expression that can be evaluated in command files
New In Version 17.0.12.
p
Edit changable (‘P’) parameters.
name
parameters
p[ ( PARAMETER [ ( ( - | .. ) PARAMETER ) | ( VALUE [ OPERATION ] ) ] ) | ( LISTVALUE [ list ] ) ]
p p 1 p 1 1.e-5 p 1 2. * p 1 - 3 p 1 .. 3 p 1 .0001 % p 1 list p 1.d-14 p *timePARAMETER
is the name or number of the parameter to be specified. See Changable (‘P’) Parameters for a list of the changeable parameters in the code and their units and default values.
VALUE
is the value to be assigned to this parameter. Note that fixed point parameters must have fixed pointed values specified, and floating point parameters must be given floating point values (i.e.,
). If VALUE is a string, this cannot be a valid float
OPERATION
add | mul | div | sub | mod | * | - | + | / | %
LISTVALUE
Value for parameter list by value. Integer or float.
Note
If the desired list value is also valid parameter number, then use the “list” keyword, otherwise it may be omitted.
Parameters are internally first set to their default values, but can be overwritten uisng input cards, e.g., in generators or interactively.
For editing parameters one may use either their number or name.
Current parameter values can be querried using the “p command by just specifying their numer or name. A range of parameters can be listed using “-” or “..”. The “*” wildcard can be used at the beginning or the end to list all parmeters with matching names where the usual UNIX shell-type maching is performed, “*” standing for any number of arbitrary characters. Parameters can be listed by matching numerical value using the “list” keyword. If the numeric value is of type float or integer and out of the allowed range of allowed parameter numbers, the “list” keyword may be omitted.
Parameters can be changed by specifying the new value or using one of the operations “*”, “-“, “+”, “/”, or “%” on the current value.
parmetercard ::= "p" listspec | setspec | vallistspec listspec ::= [ parameter [ rangeop parameter ] ] | wildspec rangeop ::= "-" | ".." wildspec ::= "*"string | string"*" | "*"string"*" setspec ::= parameter value [ operation ] vallistspec ::= value [ "list" ] parameter ::= name | number name ::= string number ::= integer value ::= float | integer | string operation ::= "add" | "mul" | "div" | "sub" | "mod" | "*" | "-" | "+" | "/" | "%"Changed In Version >15.0.0: Added matching by wildchard and parameter range.
Changed In Version 16.85.0: procession of p cards by
ttycomallows the use of parameter names in generators. Prior to that, only parameter numners were allowed in generators.Changed In Version 17.0.2: List parameters by value.
Other entry:
Useful Input Cards
newnetb
Generate new BURN network from file FILENAME.
name
parameters
newnetbFILENAME
FILENAME
Name of file from which to read definition of new network.
Note
This dates back to the early dates before ADAPNET and has not been used much in some time. Maybe use ADAPNET instead.
Map to new (bigger!) network. In contast to the genburn card in generators, only the net and netw cards are use whereas the g, gg, and m cards are not allowed. Other commands are processed as if entered on the command line.
New In Version >16.0.0.
killburn
Turn off and removes the burn co-processing.
name
parameters
killburnkillburn
inburnandimaxbare set to zero.New In Version >16.0.0.
burnamax
Print the maximum abundances reached in the BURN network.
name
parameters
burnamaxburnamaxOnly available if irecb (p 418) is set to
1.The output contains information about the mass fraction reached and the mass coordinate where it was reached.
New In Version >16.0.0.
burnaclr
Reset the recording of maximum abundances of BURN network.
name
parameters
burnaclrSee also
New In Version >16.0.0.
killpist
Reset/terminate piston.
name
parameters
killpistkillpist
mapburn
Map BURN abundances to APPROX.
name
parameters
mapburnmapburnNote
If BURN is not active, this card is ignored.
Todo
Implement in KEPLER stuff for ISE and NSE mapping?
New In Version >16.0.0.
link
Input commads from file FILENAME.
name
parameters
linkFILENAME
link ExplDFILENAME
Name of file from which to read commands.
o
Obtain/set/define optional user-defined (‘O’) parameters.
name
parameters
o[ NAME [ ( VALUE [ OPERATION ] ) | ( VALUE def ) | del ] ]
o i 1 def o i 1 + o i o o i delNAME
is the name of the parameter to be specified. By default no parameters are initilazed by KEPLER.
OPERATION
add | mul | div | sub | mod | * | - | + | / | %
These can be used in commad files or to specify other quantities that are useful to analysis later.
The plain form o without any other parameters will list all currently defined parameters.
The form with only NAME specified will return the value of the parameter.
The form with NAME and VALUE will set the parameter to the new value. The VALUE should observe the type of the parameter.
The form with NAME, VALUE, and OPERATION will perfom the operation on the parameter and set it to the resulting value. The operand VALUE should observe the type of the parameter.
Fhe form with NAME, VALUE, and def will define the new parameter and set ist value to VALUE. The variable type is inferred from the type of the initial value.
Fhe form with NAME and del will delete the optional parameter.
Note
In contrast to p and q parameters the o parameters cannot be address by number. This limitation was imposed as the parameters can be added and removed randomly.
parmetercard ::= "o" listspec | setspec | defspec | delspec listspec ::= [ parameter ] setspec ::= parameter value [ operation ] defspec ::= parameter value "def" delspec ::= parameter "del" parameter ::= name name ::= string number ::= integer value ::= float | integer operation ::= "add" | "mul" | "div" | "sub" | "mod" | "*" | "-" | "+" | "/" | "%"New In Version 17.0.2.
q
ed
Force an edit of the current cycle to be written in the ASCII output file.
name
parameters
ed[ MEDIT ]
ed 10vi:MEDIT
value to use for medit (p 276).
If MEDIT is specified, make an edit as if medit (p 276) had that value.
edp
Force a parameter edit for the current cycle to be written in the output file.
name
parameters
edpedp
end
Terminate the problem.
name
parameters
endend
fin
exit
stop
bye
quit
halt
k
kill
Immediately terminate KEPLER without the usual “shutdown procedure.”.
name
parameters
killkillNew In Version >15.0.0.
x
Write out dump file then end KEPLER.
name
parameters
xxNew In Version >16.0.0.
g
Resume normal calculations after a suspension.
name
parameters
gg
<j>
Make a current edit for zone <j> on the terminal.
name
parameters
<j>[ (i [ IONSYM ] ) | ( b [ ISOSYM ] ) | q ]
12 .5 i 1.d33 i c12 -5 b c13 0 b<j>
zone number or mass
IONSYM
symbol of ion from APPROX / NSE / QSE network
ISOSYM
symbol of species from BURN network
The usual range of zones is from
1to jm (q 2). Zone numbers less than1are counted “outward in” from the surface, with0corresponsing to the surface zone, i.e., jm (q 2) is added to the spacified number. After this, zone numbersjm (q 2) are truncated to jm (q 2) and zone numbers (now still) less than
1are truncated to1.If <j> is a float, KEPLER will try to translate it to a zone number. First, if the magnitude of the value is less than
1.e+10it is assumed the number is in solar masses. Next, values less than0.are, as above, counted from the surface, i.e., the total mass of the star, totm (q 17)summ0 (p 61) is added. KEPLER then finds the mass shell with lower boundary mass as close as possible to the provided mass coordinate.
i
make APPROX / NSE / ISE ion edit of all ions with abundances larger than abunlim (p 128)
i ISOSYM
make APPROX / NSE / ISE ion edit of the specified ion
b
make BURN species edit of all species with abundances larger than abunlimb (p 272)
b ISOSYM
make BURN species edit of the specified species
q
Make a NSE / ISE edit on the terminal
sumb
Display an edit of the mass fraction of BURN species.
name
parameters
sumb[ ( ISOSYM+ [ ZONE [ ZONE ] ] ) | ( ZONE [ ZONE ] [ISOSYM+] ) ]
sumb sumb 1 10 sumb -1. 0 c13 sumb 1 9999 sumb c12 sumb 1 c12 sumb c12 c13 sumb c12 1 1.d33 sumb c12 c13 1 1.d33 sumb 0 -10 c12 c13ZONE [ ZONE ]
Zone or zone range (inclusive) over which to sum. Similar to <j> command zone numbers out side the usual range of zones from
1to jm (q 2) are trnasformed. Zone numbers less than1are counted “outward in” from the surface, with0corresponsing to the surface zone, i.e., jm (q 2) is added to the specified number. After this, zone numbersjm (q 2) are truncated to jm (q 2) and zone numbers (now still) less than
1are truncated to1. Finally, if the first resulting number is larger then the second, the numbers are swapped.If ZONE is a float, KEPLER will try to translate it to a zone number. First, if the magnitude of the value is less than
1.e+10it is assumed the number is in solar masses. Next, values less than0.are, as above, counted from the surface, i.e., the total mass of the star, zmjm (q 2)
is added. KEPLER then finds the mass shell with lower boundary mass as close as possible to the provided mass coordinate.
If there is an overflow at the upper mass limit (ZONE
jm (q 2) for integer values or ZONE
zm
jm (q 2)
for float values) the mass lost in the wind is added. If a single zone is provided and it is beyond the maximum, only the wind is used.
ISOSYM
BURN species symbol. If supplied, only those species are edited.
If ISOSYM is not supplied, all species with abundances larger than abunlimb (p 272) are printed.
Changed In Version 17.7.5: Adjusted zone range treatment.
sumbg
Display an edit of the mass of BURN species in
g.
name
parameters
sumbg[ ( ISOSYM [ ZONE [ ZONE ] ] ) | ( ZONE [ ZONE ] [ISOSYM] ) ]
Same as sumb otherwise.
Changed In Version 17.7.5: Adjusted zone range treatment.
sumbsun
Display an edit of the mass of BURN species in
Msun.
name
parameters
sumbsun[ ( ISOSYM [ ZONE [ ZONE ] ] ) | ( ZONE [ ZONE ] [ISOSYM] ) ]
Same as sumb otherwise.
Changed In Version 17.7.5: Adjusted zone range treatment.
sumi
Display an edit of the mass fraction of APPROX / ISE / NSE ions.
name
parameters
sumi[ ( IONSYM+ [ ZONE [ ZONE ] ] ) | ( ZONE [ ZONE ] [IONSYM+] ) ]
sumi sumi 1 10 sumi -1. 0 n14 sumi 1 9999 sumi c12 o16 sumi c12 1 1.d33IONSYM
APPROX / ISE / QSE species symbol. If supplied, only those species are edited.
Same as sumb otherwise.
Changed In Version 17.7.5: Adjusted zone range treatment.
sumig
Display an edit of the mass of APPROX / ISE / NSE ions in
g.
name
parameters
sumig[ ( IONSYM [ ZONE [ ZONE ] ] ) | ( ZONE [ ZONE ] [ISOSYM] ) ]
Same as sumi otherwise.
Changed In Version 17.7.5: Adjusted zone range treatment.
sumisun
Display an edit of the mass of APPROX / ISE / NSE ions in
Msun.
name
parameters
sumisun[ ( IONSYM [ ZONE [ ZONE ] ] ) | ( ZONE [ ZONE ] [ISOSYM] ) ]
Same as sumi otherwise.
Changed In Version 17.7.5: Adjusted zone range treatment.
s
Suspend execution, or step cycle if suspended.
name
parameters
s[ N ]
s 3N
If suspended, number of cycle to run problems before suspending again.
Note
Igored if not suspended.
t
ted
Displaya ‘short’ ASCII edit on the terminal.
name
parameters
ted[ MEDIT ]
tedvi:MEDIT
value to use for medit (p 276).
If MEDIT is specified, make an edit as if medit (p 276) had that value.
time
tn
Make a nuclear reaction rate edit on the terminal (
mol/sec- over whole star).
name
parameters
tn[ REACSYM ]
tnREACSYM
reaction symbol for which to list
If REACSYM is not provided, all reactions are listed.
tq
Make a combined time and surface edit on the terminal.
name
parameters
tq
Other Terminal Edit Commands¶
e
editiso
ediso
Make an edit of the isotopic yields, summed between zones JNNER and JOUTER inclusive.
name
parameters
ediso[ JINNER [ JOUTER ] ]
ediso 171 417v:JINNER
Specification of inner zone (or mass coordinate).
v:JOUTER
Specification of outer zone (or mass coordinate).
Output is written to both on the terminal and in a special file with suffix “.yieldJINNER”. If JINNER
1, it is omitted from the suffix. This file overwrites any such existing file and is automatically sent to the laser printer (“lpr”) to be printed.Processing of zone specification is done similar to the <j> command if only JINNER is suppied, and similar to the sumb command if both both JINNER and JOUTER are supplied. I neither is supplied, the entire star is edited.
The solar abundances are read from the data file
solabu.datand the decay data and branching ratios are read fromdecay.dat. The yields and production factors are given including the wind and additionally yields and production factors are given for the wind by itself. The data formats of the filesdecay.datandsolabu.datare specified at the beginning of the existing sample files.Changed In Version >16.0.0: Works with arbitrary networks and uses decay data from
decay.dat. Include wind.
enucb
name
parameters
enucbZONE TEMPERATURE DENSITY TIMESTEP
enucb 51 1.d9 1.d6 1.ZONE
Zone from which to take composition. Processing of zone specification is done similar to the <j> command.
TEMPERATURE
temerature for flow calcualtion (
K). Use temperature from zone if set to “-“DENSITY
density for flow calcualtion (
g/cc). Use density from zone if set to “-“TIMESTEP
time step for flow calcualtion (
sec). Use current new time step dtnew (p 1) if set to “-“New In Version 17.0.1: Implemented by Laurens Keek.
Changed In Version 17.0.2: Added standardized treatment of zone specification
test
Gives a terminal edit of quantity TESTVAR for the materials in zone ZONE, but at the temperature T in
Kand density D ing/ccspecified.
name
parameters
testTESTVAR ZONE T D
test p 1 3.E+9 2.E+7TESTVAR
A variable symbol which may be anyone of the following:
value
result
k
Opacity (
cm**2/g)s
(specific) Energy Production Rate (
erg/g/sec)p
Pressure (
erg/cc)e
(specific) Energy (
erg/g)d
degeneracy parameter
ZONE
Zone from which to take composition. Processing of zone specification is done similar to the <j> command.
T
temperature T in
KD
density in
g/ccChanged In Version >16.0.0: added d to print degeneracy
tn
Make an edit of the total rate of nuclear reaction REACSYM on the terminal.
name
parameters
tnREACSYM
tn he3+he4REACSYM
Reaction Symbol
Allowed values for REACSYM are given in Zonal Nuclear Reaction Rates. The values edited are the total net rates (forward-back) summed over the whole star (in
mol/sec).
v
Make a terminal edit of the zonal edit variable denoted by EDITVAR from zones JMIN to JMAX, inclusive.
name
parameters
vEDITVAR [ JMIN [ JMAX ] ]
v ionye 1 100EDITVAR
Edit variable, see Zonal Edit Varlables.
JMIN
Single zone or lower bound of range of zones to be edited.
JMAX
Upper bound zone to be edited.
If only JMIN is specified, JMAX is assumed to be equal to JMIN. If neither JMIN or JMAX is given, then JMIN

1and JMAXjm (q 2), the index of the current outer zone. A detailed list of the allowed edit variables and their corresponiing values of EDITVAR is given in Zonal Edit Varlables.
Processing of zone specification is done similar to the <j> command if only JMIN is supplied, and similar to the sumb command if both both JMIN and JMAX are supplied.
git
Print source git repository sha-1.
name
parameters
gitgitThe output looks like this:
Git SHA-1 3a0fba8c1ef49b175c83837c0d95309aa3ba1623
uuid
Print current UUID info.
name
parameters
uuiduuidThe output looks like this:
-------------------------------------------------- VERS 170100 SHA 8267afd66f45371c2bbdf493a64804cd50cdb855 PROG 699678ba-f4d8-11e4-927c-606720611230 of Thu May 7 12:45:04 2015 EXEC 729bd3ec-f4d8-11e4-b460-606720611230 of Thu May 7 12:45:20 2015 CYCLE f7deac36-7adb-11e4-a00b-00259058e8e4 of Wed Dec 3 06:03:10 2014 DUMP 75d7ed3e-f4d8-11e4-b460-606720611230 of Thu May 7 12:45:25 2015 CYCLE 500000 FILE xxxz USER alex HOST zinc.maths.monash.edu -------------------------------------------------- VERS 170100 SHA 8267afd66f45371c2bbdf493a64804cd50cdb855 PROG 7c850138-f4da-11e4-b469-606720611230 of Thu May 7 12:59:55 2015 RUN 07b99f8a-d18b-11e3-a013-00259058e8e4 of Thu May 1 19:48:01 2014 EXEC 2e26bc6a-f4db-11e4-9e46-606720611230 of Thu May 7 13:04:53 2015 PREV f3784bde-7adb-11e4-a00b-00259058e8e4 of Wed Dec 3 06:03:02 2014 CYCLE f7deac36-7adb-11e4-a00b-00259058e8e4 of Wed Dec 3 06:03:10 2014 USER alex HOST zinc.maths.monash.eduThe first section gives the execution history (if present), the seceond the current UUID information.
The meaning of the lines is as follows:
value
result
PROGUUID of the current executable
RUNUUID of the current run
PREVUUID of the previous cycle
CYCLEUUID of the current cycle
EXECUUID of the current execution
Note
KEPLER uses Type
1UUIDs that are comopsed of time since start ot Julian Calendar (in 100 ns) and the machine MAC address.New In Version 16.85.0.
Changed In Version 17.0.4: Added execution UUID. Added execution history.
version
Type out information about the dates on which the current code modules were last modified. (deprecated).
name
parameters
versionDeprecated Since Version 16.85.0: Use uuid instead.
vf
Same as the v command except that edited values are given to
14decimal places instead of3.
name
parameters
vfEDITVAR [ JMIN [ JMAX ] ]
vf ionye 1 100
z
Makes a columnar zonal edit of up to ten EDITVAR arrays.
name
parameters
z( EDITVAR )+ [ JMIN [ JMAX ] ]
z dn tn sige sigi sigr 1 100EDITVAR
Edit variable, see Zonal Edit Varlables.
JMIN
Single zone or lower bound of range of zones to be edited.
JMAX
Upper bound zone to be edited.
If only JMIN is specified, JMAX is assumed to be equal to JMIN. If neither JMIN or JMAX is given, then JMIN

1and JMAXjm (q 2), the index of the current outer zone. A detailed list of the allowed edit variables and their corresponiing values of EDITVAR is given in Zonal Edit Varlables.
Processing of zone specification is done similar to the <j> command if only JMIN is supplied, and similar to the sumb command if both both JMIN and JMAX are supplied.
The first column in the edit gives the convection sentinel and the zone number, the second column lists the interior mass in scalem (p 273) units. Values of the requested arrays start in column 3. At least one array must be requested, up to a maximum of
10.Note
5array requests fit nicely in an80column screen window, and10fill a132column edit page.
Other ASCII Output-File Edit Commands¶
core
Show core information on screen.
name
parameters
core[ COREXLIM [ COREFELM ] ]
COREXLIM
Mass fraction limit for all core composiitons except iron. The defaulf value is
0.01.COREFELM
Iron mass fraction limit for “iron” core. The defaulf value is
0.1.The values given are the shell number (
j), interior mass (zm), radius (rn), exterior binding energy (ybind), and total entropy at the core boundary (stot). These values are displayed for the center of the star, the-jump (
drops below
0.49), the boundary of the APPROX network, theshell (maximum in energy generation by
burning), the “iron” core (defined by the mass fraction of heavy elements with mass number
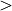
46exceeding), the
core (
mass fraction
COREFELM and
mass fraction bigger than
mass fraction), the
/
/
core (
mass fraction first drops below COREXLIM and “iron” is more abundant than COREFELM), the
/
core (
mass fraction first drops below COREXLIM and “iron” is more abundant than COREFELM), and the helium core (
mass fraction first drops below COREXLIM and iron is more abundant than COREFELM).
New In Version >15.0.0.
eostable
Write out table for EOS and opacities.
name
parameters
eostableZONE TLOW THI NTEMP DLOW DHI NRHO
eostable 1 1.E+6 1.E+9 20 1. 1.E+6 30ZONE
Zone from which to take composition. Processing of zone specification is done similar to the <j> command.
TLOW
starting temperature of table in
KTHI
ending temperature of table in
KNTEMP
number of temperature steps
DLOW
starting density of table in
g/ccDHI
ending density of table in
g/ccNRHO
number of density steps
Using the composition from zone ZONE, a table of EOS and opacity information is written into the normal ASCII output file for a logarithmic grid of temperatures (from TLOW to THI with NTEMP
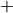
1grid points) and densities (from DLOW to DHI with NRRO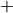
1grid points). Here TLOW and THI are inKand DLOW and DHI are ing/cc.The information written is
,
,
,
,
,
, and
, all in
cgsunits.Changed In Version 17.0.2: Fixed bug in output of
.
eostab2
Write out table for EOS with derivatives and opacities.
name
parameters
eostab2ZONE TLOW THI NTEMP DLOW DHI NRHO
eostab2 1 1.E+6 1.E+9 20 1. 1.E+6 30Parameters are the same as for eostable but the output is
,
,
,
,
,
,
,
,
, all in
cgsunits, andin
kb/baryon.New In Version >16.0.0.
Changed In Version 17.0.2: use to have
,
,
, and
.
Changed In Version 17.0.2: added treatment of specification of ZONE similar to <j>.
eostrans
Add TRANSMULT times the energy in nuclear excited states to all zonal specific energies.
name
parameters
eostranstransmult
eostrans 1.Useful in certain EOS transitions.
eoswrite
Deprecated. (See source code.).
name
parameters
eoswriteJTAB ZONE NTEMP NRRO NEOSM
Deprecated Since Version >15.0.0.
Note
The original documentation was:
EOSWRITE JTAB ZONE NTEMP NRRO NEOSM
eoswrite 626 1 20 30 10This command writes an EOS table identified by EOS # JTAB based on the composition of zone Jl, and having NTEMP temperature points and NRHO density points. This file is written after the last entry in ASCII file EOSKEP. If file EOSKEP does not exist, it is created with a sufficiently large size to contain NEOSM table sets. Before the EOSWRITE command is used, the TZ array must be set by the TV AL command so that it contains the NTEMP temperature points (in ke V), immediately followed by the NRRO density points (in g/cc). NRHO and NTEMP can sum to at most NTEMPZ (a parameter in KEPCOMS currently set to 60).
Warning
This command is no longer supported. See version
.tw:kepn:kepn3/25for the old coding if you want to try to revive it, but see eostable flfst.
flowb
Edit BURN nuclear reaction flow data.
name
parameters
flowbZONE ( TEMPERATURE | - ) ( DENSITY : - ) ( TIMESTEP | - ) [ RADIUS | + ] [ ( FILENAME | - | matrix ) ]
flowb 300 - - - + -ZONE
Zone from which to take composition. Processing of zone specification is done similar to the <j> command.
TEMPERATURE
temerature for flow calcualtion (
K). Use temperature from zone if set to “-“DENSITY
density for flow calcualtion (
g/cc). Use density from zone if set to “-“TIMESTEP
time step for flow calcualtion (
sec). Use current new time step dtnew (p 1) if set to “-“RADIUS
radius for flow calcualtion (
cm). Use radius from zone if set to “+”FILENAME
Name of output file.
If omitted, data is printed on the screen.
If the filename is “-” is specified, then the output tis written to a file with a name of the form
nameprob+ncyc (q 4)+ZONEIf the filename is matrix a diagnostic of non-zero matrix elements is printed to the screen.
Edit the BURN flows, abundances, partition functions, and reaction rates of zone ZONE for temperature TEMPERATURE (
K), density DENSITY (g/cc), and time step TIMESTEP. For neutrino exposure the radius RADIUS (cm) is used or1.e+99cmif omitted (no neutrino flux).If
TEMPERATUREorDENSITYare set to “-“, the current values of zone ZONE are used.If
TIMESTEPis set to “-“, the current new time-step dtnew (p 1) is used.If
RADIUSis set to “+”, the current value of zone ZONE is used.New In Version >16.0.0.
Changed In Version 17.0.2: Add handling of zones similar to the <j> command.
Todo
Add explanation of flow output
kapedit
Write out table for EOS and opacities.
name
parameters
kapeditZONE TLOW THI NTEMP DLOW DHI NRHO EPS
kapedit 1 1.E+6 1.E+9 20 1. 1.E+6 30 1.d-8ZONE
Zone from which to take composition. Processing of zone specification is done similar to the <j> command.
TLOW
starting temperature of table in
KTHI
ending temperature of table in
KNTEMP
number of temperature steps
DLOW
starting density of table in
g/ccDHI
ending density of table in
g/ccNRHO
number of density steps
EPS
relative change in temperature and density used for numerical derivatives
Using the composition from zone ZONE, a table of opacity information is written to the screen for a logarithmic grid of temperatures (from TLOW to THI with NTEMP
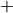
1grid points) and densities (from DLOW to DHI with NRRO
1grid points). Here TLOW and THI are inKand DLOW and DHI are ing/cc.The output is a list of temperature, density, opacity, analytical derivative of the opacity for temperature and density, respectively, numerical derivative of opacity for temperature and density, respectively, using EPS and, finally, the deviations between the numerical and analytical determinations of the derivatives. Numerical derivatives are computed by varying temperature and density by
1eps
.
Changed In Version 17.0.2: added treatment of specification of ZONE similar to <j>.
Changed In Version 17.0.11: corrected to call EOS to update quantities needed in opacity routine.
linkedit
Make an ASCII file containing terse information on structure and composition, e.g., for linking a presupemova model to Wilson (or others).
name
parameters
linkeditlinkeditFilename will be in the form
nameprob@ncyc (q 4).Deprecated Since Version >15.0.0: This is now done with external commands from the dump files using IDL or Python.
tval
Deprecated. (See source code.).
name
parameters
tvalN ( VALUE ) +
Deprecated Since Version >15.0.0.
Note
The original documentation was:
TVAL N VALl [ VAL2 VAL3 … VALl0 ]
tval 1 .1.3 1. 3. 10. 30. 100.This command sets values in the temporary array TZ such that TZ(N), TZ(N + 1), …, etc. are respectively reset to VAL1, VAL2,…etc. At least one, and up to
10values may be specified on each line. This command can be used (repeatedly if necessary) to set or change the TZ array so that it contains the NTEMP EOS table temperature points (in keV), immediately followed by the NRHO density points (in g/cc) required to specify EOS tables. (See the eoswrite command). Attempts to write beyondTZ(NTEMPZ), whereNTEMPZis a parameter currently set to60, will generate an error message.Note
This information is not saved in the restart dump.
Warning
This command is no longer supported. See version
.tw:kepn:kepn3/25for the old coding if you want to try to revive it, but see eostable flfst.
rateb
Edit the BURN reaction rates.
name
parameters
ratebTEMPERATURE DENSITY
rateb 1.d9 1.d5TEMPERATURE
desired temperature (
K)DENSITY
desired density (
g/cc)Print a table with the content of the
sigarray for temperatureTEMPERATURE(K) and densityDENSITY(g/cc).New In Version >16.0.0.
ratenub
Edit the BURN neutrino reaction rates.
name
parameters
ratenubR9 TIME
ratenub 10. 1.R9
radius location (
1.e+9 cm)TIME
time after bounce for evaluation (
sec)Print a table with the
signun(neutral current) andsignuc(charged current) arrays, and some special reaction rates) for radiusR9(1.e+9 cm) at timeTIME(sec) after bounce. IfTIMEis omitted,0.is assumed.Note
Flux goes like
and neutrinot flux decays with time.
ved
vfed
Same as the ved command except that edited values are given to
14decimal places instead of3.
name
parameters
vfedEDITVAR [ JMIN [ JMAX ] ]
vfed ionye 1 100
weightb
Print the BURN statistical weights.
name
parameters
weightb
TEMPERATUREweightb 1.d8
TEMPERATUREtemperature for evaluation (
K)The
gandwarrays are evaluated and printed for temperatureTEMPERATURE(K).New In Version >16.0.0.
wind
Print the APPROX wind information to the screen.
name
parameters
windwindNew In Version >15.0.0.
windb
Print the BURN wind information to the screen.
name
parameters
windbwindbNew In Version >16.0.0.
zed
Makes a columnar zonal edit of up to ten EDITVAR arrays and write to ASCII file. Same as z command otherwise.
name
parameters
zed( EDITVAR )+ [ JMIN [ JMAX ] ]
zed dn tn sige sigi sigr 1 100
zedit
Initiate that a special multiple column ASCII edit of the specified zonal edit variables (EDITVAR+ )to be written every NCYCZED cycles.
name
parameters
zeditIZED NCYCZED ( EDITVAR )+ [ ZEDMASSl [ ZEDMASS2 ] ]
zedit 1 50 dn tn sige sigi sigr 0. 2.IZED
Edit variable index number (max
nzedz).NCYCZED
Cycle frequency. Set to
0to terminate edits.EDITVAR
Edit variable, see Zonal Edit Varlables.
ZEDMASSl
Lower bound of mass range in scalem (p 273) units or mass coordinate (
) for which edits are made.
ZEDMASS2
Uper bound of mass range in scalem (p 273) units for which edit is made.
This command causes a special multiple column ASCII edit of the specified zonal edit variables (EDITVAR+) to be written every NCYCZED cycles. Here lZED is an index number (maximum of
NZEDZ, which currently is30, seekepcom) that distinguishes separate zedit requests, and ZEDMASSl and ZEDMASS2 specify an optional interior mass range (in scalem (p 273) units) to be edited. If only ZEDMASSl is specified, arange around it is edited, and if no masses are specified, an edit of the whole star is made. Previously specified edits can be changed or terminated by overwriting them with a new zedit command with the same index number.
Note
Setting NCYCZED

0ternlinates the edit.Note
This command is especially useful in generators.
Deprecated Since Version >15.0.0.
Other entry:
Useful Input Cards
Graphics Edit Commands¶
addiso
arange
Set the mass number range for BURN isotope plots.
name
parameters
arangeNSTART NEND
arange 1 100NSTART
lower limit of new mass number range
NEND
upper limit of new mass number range
The edit parameters minapro (p 400) and maxapro (p 401) are set to the given values. If no values are specified they are set to their default values (
-1000).
burnaplt
Plot the maximum abundances reached in the BURN network.
name
parameters
burnapltburnapltNew In Version >16.0.0.
burnmplt
name
parameters
burnmpltplot the mass coordinate where maximum abundances reached in the BURN network
burnmpltNew In Version 17.7.3.
burncplt
name
parameters
burncpltplot the cycle number when maximum abundances reached in the BURN network
burncpltNew In Version 17.7.3.
closewin
Close the graphics window.
name
parameters
closewinNew In Version >15.0.0.
listiso
List the current set of BURN species to be plotted as set by the setiso command.
name
parameters
listiso
l
Same as look.
name
parameters
lNPLOT NCYCL0 [ NCYCL1 [ NDELCYCL ] ]
Deprecated Since Version >15.0.0.
look
Make a movie (deprecated).
name
parameters
lookNPLOT NCYCL0 [ NCYCL1 [ NDELCYCL ] ]
look 31 10000 15000 1000NPLOT
plot type
NCYCL0
start cycle
NCYCL1
end cycle
NDELCYCL
cycle step (delta)
This command makes a movie of plot type NPLOT starting as closely as possible to cycle NCYCL0 and ending as closely as possible to cycle NCYCL1 at intervals as close as possible to NDELCYCL using information from the qq-files specified by setq or (by default) those available for the current problem. Plot types and output modes are as specified in the plot command and by the values of itvstart (p 127). Plot limits are assumed the same as those displayed for the current cycle by plot for this plot type, and can be adjusted using the usual graphics parameters (ipixtype (p 113)). If not specified, NCYCL1 is assumed to be equal to NCYCL0, and NDELCYCL is assumed to be the cycle interval between post-processor dump writes multiplied by idtlook (p 302).
Deprecated Since Version >15.0.0.
lprintl
Same as lpl.
name
parameters
lprintlNPLOT NCYCL0 [ NCYCL1 [ NDELCYCL ] ] [ FILENAME ]
Deprecated Since Version >15.0.0.
lpl
Make a PostScript plot of plot-type NPLOT at cycle NCYCL0 in landscape orientation on the local laser printer.
name
parameters
lplNPLOT NCYCL0 [ NCYCL1 [ NDELCYCL ] ] [ FILENAME ]
lpl 3 10000 15000 1000 s25n2a.abunNPLOT
plot type
NCYCL0
start cycle
NCYCL0
end cycle
NDELCYCL
cycle step (delta)
FILENAME
base for filenames for output
NPLOT is as defined in the plot command and use is made of infonnation from the qq-files specified by setq or (by default) those available for the current problem. If a
FILENAMEis specified, then the picture is also saved in a Postscript file with that name. If NCYCL1, or both NCYCL1 and NDELCYCL, are given (before FILENAME, if any is specified), then a series of prints will be produced starting at “look” cycle NCYCL0 and continuing to “look” cycle NCYCL1 at intervals of NDELCYCL. A ‘:’ followed by the current “look” cycle number will be appended to the FILENAME specified (but limited to a total of16characters).Deprecated Since Version >15.0.0.
lprintp
Same as lpp.
name
parameters
lprintpNPLOT NCYCL0 [ NCYCL1 [ NDELCYCL ] ] [ FILENAME ]
Deprecated Since Version >15.0.0.
lpp
Make a PostScript plot of plot-type NPLOT at cycle NCYCL0 in portrait orientation on the local laser printer.
name
parameters
lppNPLOT NCYCL0 [ NCYCL1 [ NDELCYCL ] ] [ FILENAME ]
lpp 3 10000 15000 1000 s25n2a.abunSame as lpl except paper orientation.
Deprecated Since Version >15.0.0.
maplim
Defines the limits of the timemap variables.
name
parameters
maplim[ VMINMAP YMAXMAP [ VRATMAP ] ]
maplim 7. 9. 1.e-5 'VMINMAP
new value for vminmap (p 328)
YMAXMAP
new value for vmaxmap (p 329)
VRATMAP
new value for vratmap (p 330)
This command defines the limits of the timemap variables by setting the values of parameters vminmap (p 328), vmaxmap (p 329), and vratmap (p 330). If no arguments are given, the entire range of the variable is mapped. If the specified values of VMINMAP and VMAXMAP are equal, they are reset to
1.e+99and-1.e+99, respectively, resulting in the actual range of the variable being limited only by vratmap (p 330) (see vminmap (p 328)vratmap (p 330)).
Deprecated Since Version >15.0.0: timemaps/look no longer functional
mlim
Set lower and upper limits on the relative mass coordinate used in making plots and timemaps to YMLOW and YMHI (in units of
Msun).
name
parameters
mlim[ ( [ YMLOW ] YMHI ) | old ]
mlim 2.1 10. mlim oldYMLOW
lower limit for plot relative mass coordinate
YMHI
upper limit for plot relative mass coordinate
old
restore previous values
This is accomplished by resetting yplotmin (p 134) to YMLOW
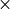
Msun/zmjm (q 2)
and yplotmax (p 135) to YMHI
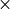
Msun/zmjm (q 2)
. If only YMHI is provided then yplotmin (p 134) is set to zm
0/zm
jm (q 2)
. If no arguments are given, or if YMLOW
YMHI, then yplotmin (p 134) is set to zm
0and yplotmax (p 135) is set to
1.. If the second argument is the flag “old” then the previous values of yplotmin (p 134) and yplotmax (p 135) are restored.Changed In Version >16.0.0: Normalization relative to mass coordinate at surface, zm
jm (q 2)
which is totm (q 17)
summ0 (p 61). Previously, normalization was with respect to total mass on grid, totm (q 17), only. Added option to call with single mass coordinate YMHI (upper limit). If no arguments were provided, yplotmin (p 134) used to be set to
0.
m
Same as mon command except that
mongois quit immediately after making the plot.
name
parameters
m( EDITVAR )+ [ AXISYL [ AXISYR ] ]
mongo
Same as mon.
name
parameters
mongo( EDITVAR )+ [ AXISYL [ AXISYR ] ]
mon
Make an X-Window MONGO plot.
name
parameters
mon( EDITVAR )+ [ AXISYL [ AXISYR ] ]
mon dn tn log linEDITVAR
Edit variable, see Zonal Edit Varlables. Up to
7may be provided.AXISYL
layout of LHS y-axix, “log”, “lin”, or “same”
AXISYR
layout of RHS y-axix, “log”, “lin”, or “same” if AXISYL is not , “same”
This command makes an X-Window MONGO plot of the first two zonal edit variables listed (EDITVAR+) vs. the mass coordinate specified by the value of parameter irtype (p 132). It leaves the user in interactive MONGO, where the graph may be modified or printed before typing “end” to return to KEPLER.
Note
Either itvstart (p 127) must be set to
1or an X Graphics Window for KEPLER must already be open (e.g., as a result of the PLOT conunand) for this command to have any effect.The mass coordinate is loaded into MONGO data column
1, and the corresponding values of each zonal edit variable, EDITAR, is loaded into MONGO subsequent data columns. At least one, and no more than seven zonal edit variables (EDllVAR+) must be specified. On entry into MONGO, graphs of the first one or two (if specified) variables are made automatically vs. the specified mass coordinate. The range of mass coordinate plotted is controlled by yplotmin (p 134) and yplotmax (p 135) which are the innermost and outermost relative mass coordinates to plot.For most quantities, the ordinate is logarithmic by default (with negative data values, or a small range of values, defaulting the plot instead to be linear), but can be set explicitly by setting AXISYL and/or AXISYR to “lin” or “log”. The code assumes that one “lin” or “log” value appended to the command line (after at least one EDITVAR) refers to AXISYL, the flag for plotting the first EDITVAR. If two “lin” or “log” values are appended, they are interpreted as AXISYL and AXISYR, the flags for plotting the first EDITVAR and second EDITVAR, respectively.
The flag “same” can also be used as the last word on the command line in order to set the axis type for plotting the second EDITVAR to be the same as for the first EDITAR, except that the axis limits are expanded to cover the extremes of both variables. “same” flag can be proceeded by at most one “lin” or “log” flag specifying the common axis type. If an axis type is not given, a default value is chosen according to the character of the data.
moncard ::= "mon" varlist yscalespec varlist ::= editvar+ yscalespec ::= [ yscale ] [ yscale | "same" ] yscale ::= "lin" | "log"Once in interactive MONGO, you can (among other things):
Type:
cursesto get mouse coordinate display, corresponding to the values of the last-defined axes.
Type:
helpto get a list of interactive MONGO commands.
Type the command sequence:
psland FILENAME play hardget a PostScript file named “
FILENAME” containing the currently displayed plot. File “FILENAME” must not already exist.Type:
endto quit interactive MONGO.
monpl
MONGO plot is printed in landscape mode on the local laser printer.
name
parameters
monpl( EDITVAR )+ [ AXISYL [ AXISYR ] ]
Like the mon command, except that the requested plot is printed in landscape mode on the local laser printer and MONGO quits, instead of the plot being displayed in an x-window and MONGO left in interactive mode.
monpp
MONGO plot is printed in portrait mode on the local laser printer.
name
parameters
monpp( EDITVAR )+ [ AXISYL [ AXISYR ] ]
Like the mon command, except that the requested plot is printed in portrait mode on the local laser printer and MONGO quits, instead of the plot being displayed in an x-window and MONGO left in interactive mode.
pt
Sampe as plot.
name
parameters
pt[ NPLOT ]
plot
Make an X-Window plot of the status of the current problem of the type specified by plot number NPLOT.
name
parameters
plot[ NPLOT ]
plot 31NPLOT
numerical plot layout (see ipixtype (p 113))
Note
Either itvstart (p 127) must be set to
1or an X Graphics Window for KEPLER must already be open (e.g., as a result a previous plot command) for this command to have any effect.Currently allowed values of NPLOT are the same as those allowed for parameter ipixtype (p 113) and produce the same types of plots.
printl
Same as pl command.
name
parameters
printl[ NPLOT ] [ FILENAME ]
pl
Make a PostScript plot of the current problem status in landscape orientation.
name
parameters
pl[ NPLOT ] [ FILENAME ]
pl pl 31 pl myplot.ps pl 31 myplot.ps pl myplot.ps 31NPLOT
numerical plot layout (see ipixtype (p 113))
FILENAME
filename to which the plot is made
NPLOT is the plot type defined in the same way as in the plot command. If NPLOT is not specified, it is taken to be ipixtype (p 113).
If FILENAME is specified, the picture is saved in a PostScript file with that name, if omitted, it is printed on the local laser printer instead.
Changed In Version >15.0.0: Removed automatic printing and file name generation.
Changed In Version 17.0.2: FILENAME can be specified without specifying NPLOT
Note
The original documentation states:
If 'ok' is given for FILENAME, a new file-name is generated automatically in the form NAMEPROB:NCYC, where NAMEPROB is the current problem name and NCYC is the current cycle.
pp
Samme as printp.
name
parameters
pp[ NPLOT ] [ FILENAME ]
printp
Make a PostScript plot of the current problem status in portrait orientation.
name
parameters
printp[ NPLOT ] [ FILENAME ]
pp 31 myplot.psSame as pl excpet orientation.
setiso
Sets the detailed isotopic abundances to be plotted by the “plot
6” or “look6” commands.
name
parameters
setiso
ISOSYM{1,50}setiso h1 he4 c12 016 mg25 a126ISOSYM
symbol of species from BURN network
At least
1and no more than50isotopic symbols must be specified from the set of current BURN isotopic symbols.
setlib
Set the dump library file and associated parameters to be used in making time-plots.
name
parameters
setlib[ NAMETLIB [ NCYCT0 [ NCYCT1 [ NCYCTDEL [ NCYCQQT [ LENTDMPT [ NIYMAXT ] ] ] ] ] ] ]
setlib s25s2a.lib 0 18345 10 5 384 20000NAMETLIB
Name of desired dump library file. The default is the one for the current job.
NCYCT0
First dump cycle to be read and plotted. Default is
0.NCYCT1
Last dump cycle to be read and plotted. Default is last cycle in dump library.
NCYCTDEL
The interval in dump cycles between dump library reads. Default is ncycqq (p 299).
NCYCQQT
Number of cycles between dump library dumps. Default is ncycqq (p 299).
LENDMPT
Length of each time dump in
NAMETLIB. Default is384.NIYMAXT
Maximum number of
IYcoordinate values inNAMETLIB. Default is20000.If setlib is not called, the default values are set when timeplot or tp is first called. Calling setlib without arguments resets all these variables to their default values if they have previously been changed by a setlib command.
Deprecated Since Version >15.0.0.
setq
Set the names of the qq-files to be post-processed by other commands such as look, lprintl, etc.
name
parameters
setq[ NAMEQQL0 [ NAMEQQLl ] ]
setq s25s2a.qa s25s2a.qkNAMEQQL0
first member of the sequence of qq-files to be read
NAMEQQL1
last member of the sequence of qq-files to be read
When used without arguments, setq implies that all the qq files for the current problem in the current working directory are to be used.
Note
This is the default situation for most post-processing commands and that setq only has to be used in this mode to restore the specified qq-files to this default.
If only NAMEQQL0 is specified, all available qq-files in the sequence starting with NAMEQQL0 will be read.
Note
qq-file names can be up to
16characters long (at least on UNIX machines) and need not be those generated by the current problem.Deprecated Since Version >15.0.0.
tm
Same as timemap.
name
parameters
tmNAMEVAR [ LOGFLAG [ NCYCL0 [ NCYCL1 [ NDELCYCL ] ] ] ]
Deprecated Since Version >15.0.0.
timemap
Makes a space-time map for zonal edit variable NAMEVAR starting as closely as possible to cycle NCYCL0 and ending as closely as possible to cycle NCYCL1.
name
parameters
timemapNAMEVAR [ LOGFLAG [ NCYCL0 [ NCYCL1 [ NDELCYCL ] ] ] ]
timemap convect lin 0 18750 1NAMEVAR
name of plot variable from qq file
LOGFLAG
specify the desired scaling for the variable being displayed, “log” or “lin”
NCYCL0
start cycle
NCYCL1
end cycle
NDELCYCL
cycle step (delta)
Uses information from the qq-files specified by setq or (by default) those available for the current problem.
The mass coordinate axis type and limits is set by the same parameters as for normal KEPLER plots. For details, see the comments for the
timemaproutine for other relevant input parameters.If not specified, NCYCLl, is assumed to be the last cycle for which infonnation is available in the qq-files specified by setq, and NDELCYCL is assumed to be the cycle interval between post-processor dump writes multiplied by idtlook (p 302). If a colormap whose name is in the form, NAMEVAR.map (e.g., “
convect.map”), is available in the local directory (or as a second alternative, is in the directory “/usr/local/map”), it will be used to make the plot. Otherwise a simple default rainbow-style map, “usr/local/map/spectral.map”, will be used. After the plot is made, the user can manipulate it further (including changing to a new variable and/or color map) by using the menus displayed when the right mouse button is depressed. Depressing the left mouse button displays an overlay rectangle that can be positioned and/or stretched to indicate a time-space region to zoom into and replot.Warning
This command currently only works on a Silicon Graphics terminal.
Deprecated Since Version >15.0.0.
tp
Same as timeplot.
name
parameters
tp( TIMEVAR )+ [ AXISYL AXISYR ]
Deprecated Since Version >15.0.0.
timeplot
Make an X-Window plot of the first two time-edit variables listed (TIMEVAR+) vs. the time coordinate specified by the value of maptime (p 327).
name
parameters
timeplot( TIMEVAR )+ [ AXISYL AXISYR ]
timeplot eni enk enp log sameTIMEVAR
Name of plot variable from qq file. Up to
7may be provided.AXISYL
layout of LHS y-axix, “log”, “lin”, or “same”
AXISYR
layout of RHS y-axix, “log”, “lin”, or “same” if AXISYL is not , “same”
Leaves the user in interactive MONGO, where the graph may be modify or printed before typing “end” to return to KEPLER.
Note
Either itvstart (p 127) must be set to
1or an X Graphics Window for KEPLER must already be open (e.g., as a result of the plot command) for this command to have any effect.Unless a setlib command has previously been issued to the contrary, the time histories for these variables are read from the “.lib” file for the current problem for the entire range of available cycles. The time coordinate is loaded into MONGO data column
1, and the corresponding time sequence for each timeplot variable, TIMEVAR, is loaded into subsequent MONGO data columns. At least one, and no more than seven time-edit variables (TIMEVAR) must be specified.The range of the time coordinates plotted is controlled by timecmin (p 321) and timecmax (p 322) and defaults to the entire available range. For most quantities, the ordinate is logarithmic by default (with negative data values or a small range of values defaulting the plot instead to linear), but axis type can be set explicitly by setting AXISYL and/or AXISYR to “
lin” or “log”. The code assumes that one “lin” or “log” value appended to the command line (after at least one TIMEVAR) refers to AXISYL, the flag for plotting the first TIMEVAR. If two “lin” and/or “log” values are appended, they are interpreted as belonging to the first and second TIMEVAR, respectively. The flag “same” can also be used as the last word on the command line in order to set the axis type for plotting the second TIMEVAR to be the same as for the first TIMEVAR, except that the axis limits are expanded to cover the extremes of both variables. The “same” flag can be proceeded by at most one “lin” or “log” flag specifying the common axis type. If an axis type is not given, a default value is chosen according to the character of the data.timeplotcard ::= "timeplot" varlist yscalespec varlist ::= timevar+ yscalespec ::= [ yscale ] [ yscale | "same" ] yscale ::= "lin" | "log"Once in interactive MONGO, you can (among other things):
Type:
cursesto get mouse coordinate display, corresponding to the values of the last-defined axes.
Type:
helpto get a list of interactive mongo commands.
Type the command sequence::
psland FILENAME play hardto get a PostScript file named FILENAME containing the currently displayed plot. File FILENAME must not already exist.
Type:
endto quit interactive MONGO.
Deprecated Since Version >15.0.0.
tppl
Like the timeplot command, except that the requested plot is printed in landscape mode on the local laser printer and MONGO quits, instead of the plot being displayed in an x-window and MONGO left in interactive mode.
name
parameters
tppl( TIMEVAR )+ [ AXISYL AXISYR ]
Deprecated Since Version >15.0.0.
tppp
Like the timeplot command, except that the requested plot is printed in portrait mode on the local laser printer and MONGO quits, instead of the plot being displayed in an x-window and MONGO left in interactive mode.
name
parameters
tppp( TIMEVAR )+ [ AXISYL AXISYR ]
Deprecated Since Version >15.0.0.
tlim
Set limits on the time coordinate used in making timeplots and timemaps by resetting the values of TIMECMIN and TIMECMAX to the specified values.
name
parameters
tlim[ ( TIMECMIN TIMECMAX ) | old ]
tlim -15.3 -10. tlim oldTIMECMIN
lower limit for time coordinate used in time plots
TIMECMAX
upper limit for time coordinate used in time plots
old
restore previous values
If no arguments are given or if TIMECMIN
TIMECMAX, then all available time points are plotted.
Note
Time-coordinate units are specified by maptime (p 327) and must be floating point numbers.
If the second argument is the flag “old” then the previous values of timecmin (p 321) and timecmax (p 322) are restored.
Deprecated Since Version >15.0.0: No longer used/needed.
ylim
Sets the y-axes limits on MONGO plots.
name
parameters
ylim[ YLLOWMON YLHIMON [ same | ( YRLOWMON YRHIMON ) ] ]
ylim 3. 5. ylim 3. 5. same ylim 3. 5. 0.44 0.5YLLOWMON
lower limit for the variable plotted on the left-hand y-axis
YLHIMON
upper limit for the variable plotted on the left-hand y-axis
YRLOWMON
lower limit for the variable plotted on the right-hand y-axis
YRHIMON
upper limit for the variable plotted on the right-hand y-axis
same
if specified in place of the right-hand y-axis limits, those will be set to be the same as for the left-hand y-axis
If no arguments are specified for a given axis, or if their high and low values are equal, then the entire range of the corresponding variable will be plotted.
Abundance and Production Factor Plots¶
pf
Plot production factor of all stable isotopes relative to solar after decay.
name
parameters
pf[ approx | burn | wind | ( ZSTART [ ZEND ] ) ]
pf pf wind pf 1 9999approx
everything in the APPROX network plus the wind is summed up
burn
everything that is processed by the BURN network, i.e., that has a mass coordinate at the base of the zone bigger than bmasslow (p 419), plus the wind is summed up
wind
only the wind is summed up
ZSTART
Single zone or lower bound of range of zones to be summed.
ZEND
Upper bound zone to be summed.
If only ZSTART is specified, ZEND is assumed to be equal to ZSTART. If neither ZSTART or ZEND is given, then ZSTART

1and ZENDjm (q 2), the index of the current outer zone.
If only ZSTART is supplied, processing of zone specification is done similar to the <j> command. If the resulting zone is beyond the outer boundary of the star, the wind “zone” is summed up.
0corresponds to just the surface zone.If both both ZSTART and ZEND are supplied, processing is similar to the sumb command. If there is an “overflow” (one of the processed zone specifications is beyond the outer boundary of the star), the wind is included. That is, to include everything in star above a given shell number but excluding the wind,
0(zero) should be chosen as upper boundary. If both ZSTART and ZEND are beyon the upper edge of the star, then only the wind shown.New In Version >16.0.0.
Changed In Version 17.0.2: Genral processing of zone specifications
YD
Plot mass of all stable isotopes after decay (
Msun).
name
parameters
YD[ approx | burn | wind | ( ZSTART [ ZEND ] ) ]
YD YD approx YD 1 0Same as pf otherwise.
New In Version >16.0.0.
Changed In Version 17.0.2: Genral processing of zone specifications
yd
Plot mass fraction of all stable isotopes after decay.
name
parameters
yd[ approx | burn | wind | ( ZSTART [ ZEND ] ) ]
yd yd approx yd 1 0Same as pf otherwise.
New In Version >16.0.0.
Changed In Version 17.0.2: Genral processing of zone specifications
Y
Plot mass of all isotopes (
Msun).
name
parameters
Y[ approx | burn | wind | ( ZSTART [ ZEND ] ) ]
Y windStable isotopes are indicated by filled circles, unstable isotopes are shown as hollow circles.
Same as pf otherwise.
New In Version >16.0.0.
Changed In Version 17.0.2: Genral processing of zone specifications
y
Plot mass fraction of all isotopes.
name
parameters
y[ approx | burn | wind | ( ZSTART [ ZEND ] ) ]
y windSame as y otherwise.
pfe
Plot production factor of all elements relative to solar after decay.
name
parameters
pfe[ approx | burn | wind | ( ZSTART [ ZEND ] ) ]
pfe pfe burnSame as pf otherwise.
New In Version >16.0.0.
Changed In Version 17.0.2: Genral processing of zone specifications
pfa
Plot production factor of all isobars relative to solar after decay.
name
parameters
pfa[ approx | burn | wind | ( ZSTART [ ZEND ] ) ]
pfa pfa burnSame as pf otherwise.
New In Version >16.0.0.
Changed In Version 17.0.2: Genral processing of zone specifications
ya
Plot yield of all isobars.
name
parameters
ya[ approx | burn | wind | ( ZSTART [ ZEND ] ) ]
ya ya burnSame as pf otherwise.
New In Version >16.0.0.
Changed In Version 17.0.2: Genral processing of zone specifications
yda
Plot yield of all isobars relative after decay.
name
parameters
yda[ approx | burn | wind | ( ZSTART [ ZEND ] ) ]
yda yda burnSame as pf otherwise.
New In Version >16.0.0.
Changed In Version 17.0.2: Genral processing of zone specifications
YE
Plot mass of all elements (
Msun).
name
parameters
YE[ approx | burn | wind | ( ZSTART [ ZEND ] ) ]
YESame as pf otherwise.
New In Version >16.0.0.
Changed In Version 17.0.2: Genral processing of zone specifications
YA
Plot decayed mass of all isobars (
Msun).
name
parameters
YA[ approx | burn | wind | ( ZSTART [ ZEND ] ) ]
YASame as pf otherwise.
New In Version >16.0.0.
Changed In Version 17.0.2: Genral processing of zone specifications
YDE
Plot mass of all elements after decay (
Msun).
name
parameters
YDE[ approx | burn | wind | ( ZSTART [ ZEND ] ) ]
YDESame as pf otherwise.
New In Version >16.0.0.
Changed In Version 17.0.2: Genral processing of zone specifications
YDA
Plot mass of all isobars after decay (
Msun).
name
parameters
YDA[ approx | burn | wind | ( ZSTART [ ZEND ] ) ]
YDASame as pf otherwise.
New In Version >16.0.0.
Changed In Version 17.0.2: Genral processing of zone specifications
Ye
Plot decayed mass of all elements (
Msun).
name
parameters
Ye[ approx | burn | wind | ( ZSTART [ ZEND ] ) ]
Special Purpose Commands¶
null
Do nothing.
name
parameters
null
*
Execute special section from command file.
name
parameters
*SENTINEL
* t9SENTINEL
sentinel of specila section to execute
If a the command file contains a specila section, e.g.,
* t9 d #t9 endthis would be executed with the sample command given above.
Note
If the special section does not exits, nothing happens and no error is issued.
New In Version 17.0.2.
/
Add command after “
/” at the end of command file.
name
parameters
/COMMAND
/ * / @tn(1)>1.d9 / d #tc9 / endCOMMAND
string to add to command file
See the page on command files for command file name resolution rules.
New In Version 17.0.2.
Other entry:
Useful Input Cards
!
Re-execute previous command from history.
name
parameters
![ NUMBER ]
! 3NUMBER
Number of how many command back to re-execute. The default is
1.A better way of doing this including editing of previous commands is to use
rlwrap, e.g., staring KEPLER usingrlwrap kepler s12#presn sNew In Version >16.0.0.
!!
Lists the last commands, last command last, and their number in the list.
name
parameters
!!This is useful in combination the ! command.
New In Version >16.0.0.
adapnet
Manually call subroutine
adapnetto adapt network.
name
parameters
adapnetNew In Version >16.0.0.
addatmos
Add an isothermal, exponential atmosphere to the surface of the star.
name
parameters
addatmosNATMOS RHOATM1 [ TEMPATM ]
addatmos 10 3.e-12NATMOS
number of atmosphere zones
RHOATM1
cut-off sensity for atmosphere
TEMPATM
temperature of atmosphere
The atmosphere consists of NATMOS zones and extending out to a density of RHOATM1 (
g/cc). The atmospheric conditions are scaled from the surface gravity, density, temperature and radius of the outer zone. The atmosphere is assumed to be thin (slab-like) compared to the star’s radius and its composition is taken to be the same as that of the outer zone. If TEMPATM (K) is specified, it is used instead of the temperature of the outer zone in constructing the atmosphere.
addlook
Add zonal edit variable EDlTVAR to the list of “look” variables that subroutine
READQreads from the qq dump files.
name
parameters
addlookEDITVAR [ delete ]
addlook sneut deleteEDITVAR
Edit variable, see Zonal Edit Varlables.
delete
EDITVAR is deleted from the list of look variables instead of added.
Note
All current commands such as plot automatically load their own ‘look’ lists and then return the list to its original state when they are finished. Future commands, however, may require the use of addlook.
Deprecated Since Version >15.0.0.
addsurf
Add isothermal surface zones with specified properties.
name
parameters
addsurf[ MSURF | ( NSURF TMSURF TEMPSURF RHOSURF VELSURF [ AWSURF ] ) ]
addsurf 10 1.E+32 1.E+4 1.E-11 0.MSURF
Amount of mass to add as a single zone (
g)NSURF
number of zones to be added
TMSURF
total mass of zones to be added (
g)TEMPSURF
temerature of zones
RHOSURF
density of zones
VELSURF
velocity of zones
AWSURF
velocity of zones
Add NSURF zones of equal mass totaling TMSURF total mass (
g) with temperature, TSURF (K), density, RHOSURF (g/cc), velocity, VELSURF (cm/sec), and the composition last specified by the compsurf command.If (only) MSURF is specified, zone of this mass (
g) will be accreted and xmacrete (p 212) will be reduced by this amount or set to0if MSURFxmacrete (p 212).
If no parameter is given, the mass of the current “phantom zone” xmacrete (p 212) is added as a new zone to the grid and xmacrete (p 212) is set to zero.
If AWSURF is not provided, the value from the outermost zone is used.
Note
Each time addsurf is called, the sum of the mass fractions in the
compsurfarray is normalized to unity.Changed In Version >16.0.0: Add MSURF and call variant without options.
Changed In Version 17.9.16: Add AWSURF
alias
Define alias.
name
parameters
alias
NAMEA“COMMAND-STRING”alias tl "tq, 1, 1 i"
NAMEAname of alias to (re)define
”COMMAND-STRING”
command sting, less than
71characters longNote
COMMAND-STRING must be enclosed in double quotes
Define alias NAMEA to invoke the command string COMMAND-STRING. COMMAND-STRING must be enclosed in double quotes and be less than
71characters long. The command string may be a series of comma-delimited TTY commands. Note that the entire alias command may not exceed80characters and may not, itself, be comma-delimited. There is a limit of200(ncsavedz) total aliases.
adzone
Manually adzone zones ZONE
ZONE
1to zones ZONEZONE
2.
name
parameters
adzoneZONE
dezone
Manulally dezone zones ZONE
ZONE
2to zones ZONEZONE
1.
name
parameters
dezoneZONE [ - ]
alliso
Generate a BURN network that contains all isotopes from the
bdatfile (plusp,n,he4).
name
parameters
allisoallisoUseful for debugging purposes. For real simulations use the adaptive network instead.
New In Version >16.0.0.
box
Change the output box number to BOX#.
name
parameters
boxBOX#
box v9SBOX#
new output box numer, three character symbol
Deprecated Since Version >15.0.0.
bstat
Print out current BURN statistics and timing information.
name
parameters
bstatbstatNew In Version >16.0.0.
burn
Do BURN processing of zone
1according to provided history file.
name
parameters
burnDATAFILE
burn burndata.datDATAFILE
file with burn history data
Note
Not yet implemented.
addwind
Add wind surface zones.
name
parameters
addwindNWIND WINDMASS RATEWIND VELWIND [ VESCMULT [ TEFFWIND [RADPWIND [AWWIND] ] ] ]
addwind 5 1.0e-5 1.e-4 10. 1. 3.098e+3 3.443e+13NWIND
number fo wind zones to add
WINDMASS
total mass of wind (
Msun)RATEWIND
mass-loss rate (
Msun/yr)VELWIND
wind terminal velocity (
km/sec)VESCMULT
escape-velocity multiplier
TEFFWIND
effective photospheric temperature (
K)RADPWIND
radius used (
cm)AWWIND
angular velocity of wind zones (
rad/sec)Add NWIND zones of equal mass totaling WINDMASS (
Msun) with mass-loss rate RATEWIND (Msun/yr), terminal velocity VELWIND (km/sec). Optional inputs are the escape-velocity multiplier, VESCMULT (default1.) and the effective photospheric temperature TEFFWIND (K) and radius RADPWIND (cm) used in generating the wind profile. The mass-loss rate is assumed to stay constant at RATEWIND during the time these zones “took” to leave the surface of the star, and the velocity at any point is the sum of the local escape velocity times VESCMULT and the wind’s terminal velocity, VELWIND. The wind’s local temperature is calculated by assuming that it is in LTE with the photosphere specified by TEFFWIND and RADPWIND. If no explicit values of these photospheric variables are given, they default to the existing photospheric temperature (teff (q 48)) and radius (radius (q 47)). The composition of the wind is taken to be the same as that of the outer zone. If AWWIND is not provided, the value form the outermost zone is used.Note
Several addwind commands can be used in succession to build up a wind with a time-dependent mass-loss rate, or to achieve non-constant-mass zoning.
Changed In Version 17.9.16: Add AWWIND
check
Type out the number of errors (
NIOERR) the code has encountered sending out ASCII output files since the last restart.
name
parameters
checkWarning
This command is only meaningful on a CRAY computer.
Deprecated Since Version >15.0.0.
chngcomp
Change the composition in zones JMIN through JMAX.
name
parameters
chngcompZONE ZONE [ ZONEORG | ( FIRSTION# ( MFRAC )+ ) | ( MFRAC ION )+ ]
chngcomp 10 20 1 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. .5 0. .5 chngcomp 0 -10 -11 chngcomp 0. 1. 0.JMIN JMAX
Zone range (inclusive) in which to change composition. Processing of the zone specifications is done the same way as for the sumb command.
ZONEORG
Zone from which to copy composition. Processing of the zone specifications is done the same way as for the <j> command.
FIRSTION#
number of first ion in APPROX network
MFRAC
new mass fraction of ion
ION
name of ion from APPROX network
Change the composition in zones JMIN through JMAX to the ion mass fractions specified. At least one and up to eight mass fractions can be given on the command line. The compositions changed begin with that of the ion corresponding to APPROX ion number FIRSTION# and continue on in ion number order. All other mass fractions are set to
0..Alternatively, ions can be specified ion-by-ion giving pairs of mass fraction, MFRAC, and the APPROX ion name, ION.
If an orgin zone, ZONEORG is specified, the composiiton information from that zone is copied.
If no ions are specified, the information currently stored in the
xnwcomparray is used to set the composition of the zones. The information in that array can be changed using the setcomp and copycomp commands and be viewed using the prncomp command.setcomp clear setcomp 6 .5 setcomp 8 .5 prncomp chngcomp 10 20Mass fractions will be renonnalized to sum to unity, and the equation of state will be recomputed for the new composition. All old abundance information from these zones is disregarded. Check zonal compositions afterwards using the “<j> i” command.
Warning
Radically altering the composition in any zone may cause discontinuous changes in its internal energy, pressure, etc. and lead to convergence problems. Take special care in degenerate cases. The newe command may be useful here.
Note
The user takes full responsibility for any misleading and/or unphysical results that may be produced due to the use of this command.
Warning
BURN abuncaes are not copied in the present version. Hence this command should not be used with lburn (p 434)

1, with iburnye (p 357)
1, or just with BURN in general.Changed In Version 17.0.2: Added generalized zone specification. Added automatic resetting of
xnwcompif mass fractions are specified.Note
The command description used to state:
::Non-specified abundances are given whatever garbage values may have initially been in xnwcomp and multiple use of this command is complicated by the fact that the mass fractions of the current contents of the xnwcomp array are renormalized to unity after each use.
Repeated use of this command can set all the elements in the XNWCOMP array in subroutine TTYCOM (which is then used to change the zonal abundances).
compsurf
Set the mass fraction values in the
compsurfarray.
name
parameters
compsurf[ ( FIRSTION# ( MFRAC )+ ) | ( MFRAC ION )+ | ZONEORG | clear | show ]
compsurf compsurf -1 compsurf -1. compsurf clear compsurf 1 0. .7 0. 0. .28 0. .02 compsurf show number of first ion in |APPROX| :ref:`network <ion>`MFRAC
new mass fraction of ion
ION
name of ion from APPROX network
ZONEORG
Zone from which to copy composition. Processing of the zone specifications is done the same way as for the <j> command.
clear
reset
compsurfarray to all0.show
show current content of
compsurfarrayThese compositions are used to set the composition of the surface zones added by the addsurf command.
Starting with its FIRSTION#th entry, set the values of subsequent entries of the
compsurfarray inkepcomequal to the list of MFRAC+ vlaues given. At least one, and up to10such values can be given on each command line. Repeated use of this command can thus set all the elements of thecompsurfarray. The compositions are numbered corresponding to APPROX ion number.Alternatively, ions can be specified ion-by-ion giving pairs of mass fraction, MFRAC, and the APPROX ion name, ION.
If just ZONEORG is given, the composition of that zone is used to initialize the
compsurfarray.If no parameter is specified, the composition of the outermost zone is used to initialize the
compsurfarray.Warning
It is quite useful to use the clear option to reset the
compsurfarray before setting values. If that has not been done before, the content of the array may be undefined.Note
This array is stored in the restart dump for later use.
Note
Note that by default the abundances of the outermost zone are copied in the surface composition vectors on problem generation so that, if this is desired, no additional compsurf or compsurb commands are required.
New In Version >16.0.0.
Changed In Version 17.0.2: Added to allow multiple ion abundances simialr to the generator m card.
Changed In Version 17.0.2: The undocumented behavior that compsurf without argumnets also does the same operation for
compsurfbhas been discontinued.
cpzone
Copy composition from zone ZONE_FROM to zone range specified by ZONE_TO_LOW and ZONE_TO_HIGH.
name
parameters
cpzoneZONE_FROM ZONE_TO_LOW ZONE_TO_HIGH [ MODE ]
cpzone 107 1 106 ltgZONE_FROM
Zone from which to copy composition and thermodynamic properties (if requested). Processing of the zone specifications is done the same way as for the <j> command.
ZONE_TO_LOW ZONE_TO_HIGH
Zone range (inclusive) in which to change composition and thermodynamic properties (if requested). Processing of the zone specifications is done the same way as for the sumb command.
MODE
Specifies the adjustment of thermodynamics on the copied zone. If omitted, the zone temperatures is not changed.
Currently all modes by default keep the zone density. Otherwise zone radii in the entire star would have to be adjusted.
The following values for temperature extrapolation are implemented:
value
result
(none)
keep temperature
ct
copy temperature of ZONE_FROM
ita
ideal gas temperature extrapolation adiabatic (
)
rta
relativistic gas temperature extrapolation adiabatic (
)
ltg
local gradient temperature extrapolation
tpn
temperature exponent to fit pn
ZONE_TO_LOW
h
adjust temperature to get same pressure and density
New In Version >16.0.0.
Note
Useful to convert a last bit of fuel in the center if a low-mass star to the compostion of the layers above.
cnviso
Convert fraction FRACTIO of BURN isotope ISO_FROM to BURN isotope ISO_TO in zones ZONE_START to ZONE_END.
name
parameters
cnvisoISO_FROM ISO_TO FRACTION ZONE_START ZONE_END
conviso c13 c12 1. 1 0ISO_FROM
source isotope symbol
ISO_TO
target isotope symbol
FRACTION
fraction of isotope to convert
ZONE_START ZONE_END
Zone range (inclusive) in which to change composition. Processing of the zone specifications is done the same way as for the sumb command.
Warning
At this time, this is all that happens; APPROX is not updates, neither are any thermodynamic quantities. Therefore you should use this command only with small mass fractions.
New In Version >16.0.0.
Changed In Version 17.0.2: Added general processing of zone specifications.
clampvel
Limit magnitude of velocity.
name
parameters
clampvelVELOCVITY
clampvel 1.d9VELOCITY
maximum magnitude of allowed velocity
All velocties with larger absolute value are truncated.
New In Version >15.0.0.
compsurb
Set the mass fraction values in the
compsurfbarray.
name
parameters
compsurb[ ( FIRSTION# ( MFRAC )+ ) | ( MFRAC ION )+ | ZONEORG | clear | show ]
compsurb .02 n14 .7 he4 .28 he4Same behaviour as compsurf but for the BURN isotope array
compsurfb.New In Version >16.0.0.
mapsurfb
Map
compsurfbarray tocompsurfarray.
name
parameters
mapsurfb
copycomp
Setup
xnwcomparray by copying the composition information from ZONEORG.
name
parameters
copycompZONEORG
scalewnd
Scale wind array.
name
parameters
scalewndscalewndHelp procedure to correct a bug in versions before 15.23. Both,
windandwindbarrays are updated.New In Version 15.23.0.
Deprecated Since Version >15.23.0.
Note
may be removed if no longer needed
addwnd
Add mass to
windarray.
name
parameters
addwndIONSYM MASS
addwnd c12 1.37d33IONSYM
symbol of ion to which mass is added in
windarrayMASS
amount of mass to add.
Help procedure to correct a bug in versions before 15.23
New In Version 15.23.0.
Deprecated Since Version >15.23.0.
Note
may be removed if no longer needed
addwndb
Add mass to
windbarray.
name
parameters
addwndbIONSYM MASS
addwnd c12 1.37d33IONSYM
symbol of ion to which mass is added in
windarrayMASS
amount of mass to add.
Help procedure to correct a bug in versions before 15.23
New In Version 15.23.0.
Deprecated Since Version >15.23.0.
Note
may be removed if no longer needed
cutbin
Manually truncate binary output files to current cycle.
name
parameters
cutbincutbinNote
The use of this command should rarely be necessary in current KEPLER as the binary output files (e.g.,
nameprob.cnv) are truncated to the current cycle automatically on restart of the problem.In the past, all records were kept and removing the duplicate and superfluous ones was left to the reading routine or external tools.
newbin
Delete all output files (
*.cnv, etc.) and reset all convection plot and wind parameters and version numbers to current default values.
name
parameters
newbin
pulsar
Print the estimated pulsar rotation rate.
name
parameters
pulsarPSRMB
PSRMB
the pulsar baryonic mass (
Msun). If not specified, a value of1.7Msunis assumed.It is assumed all angular momentum is conserved during collapse and that the neutron star has a gravitational mass of
1.4Msun, a radius of12km, and a moment of inertia of0.36.
prncomp
Print the content of the
xnwcomparray.
name
parameters
prncompSee also
New In Version >16.0.0.
qset
Overwrite value of q parameter.
name
parameters
qsetQPARM VALUE
setq 1 1.QPARM
Name or number of q parameter to change.
VALUE
New value of parameter. Must be of correct type.
Warning
You should not have to use this.
New In Version 17.0.2.
setcomp
Set the mass fraction values in the
xnwcomparray.
name
parameters
setcomp( FIRSTION# ( MFRAC )+ ) | ( MFRAC ION )+ | ZONEORG | clear | show
setcomp -1 setcomp -1. setcomp clear setcomp 1 0. .7 0. 0. .28 0. .02 setcomp show number of first ion in |APPROX| :ref:`network <ion>`MFRAC
new mass fraction of ion
ION
name of ion from APPROX network
ZONEORG
Zone from which to copy composition. Processing of the zone specifications is done the same way as for the <j> command.
clear
reset
xnwcomparray to all0.show
show current content of
xnwcomparray. Same as prncomp.These compositions are used to set the composition of the surface zones added by the addsurf command.
Starting with its FIRSTION#th entry, set the values of subsequent entries of the
xnwcomparray inkepcomequal to the list of MFRAC+ vlaues given. At least one, and up to10such values can be given on each command line. Repeated use of this command can thus set all the elements of thexnwcomparray. The compositions are numbered corresponding to APPROX ion number.Alternatively, ions can be specified ion-by-ion giving pairs of mass fraction, MFRAC, and the APPROX ion name, ION.
If just ZONEORG is given, the composition of that zone is used to initialize the
xnwcomparray in the same was as copycomp.Warning
It is quite useful to use the clear option to reset the
xnwcomparray before setting values. If that has not been done before, the content of the array may be undefined.Note
This array is stored in the restart dump for later use.
New In Version >16.0.0.
Changed In Version 17.0.2: Add isotopes by ion name.
setcycle
Change the cycle number stored in ncyc (q 4).
name
parameters
setcycleNCYC
setcycle 1000NCYC
new value for ncyc (q 4)
Was introduced for managment of cnv files. Now used to reset problems, e.g., after an XRB simulation si brough into equilibrium.
New In Version >15.0.0.
cutsurf
Remove zones outside ZSURF from the surface of the star.
name
parameters
cutsurf[ ZSURF ] [ - | + ]
cutsurf - cutsurf -3 - cutsurf 511ZSURF
zone above which to cut surface layers
+
keep tbound (p 68) unchanged but update pbound (p 69)
-
keep both tbound (p 68) and pbound (p 69) unchanged
pbound (p 69) and tbound (p 68) are automatically reset to correspond to the innermost zone removed unless the flag - or + are specified. When + is specified, only pbound (p 69) is updated whereas tbound (p 68) remians unchanged. Processing of zone specification ZSURF is done similar to the <j> command. If ZSURF is not specified, one zone is cut from the surface.
This option is sometimes useful in removing essentially “frozen” outer layers of the star so that available zones can be concentrated on core processing or to remove high velocity surface zones that are trying to form a stellar wind.
The APPROX and BURN abuncanes in the truncated zones are added to the
windandwindbarrays.Changed In Version 16.0.0: Truncated mass is added to
windandwindbarrays.Changed In Version >16.0.0: Added - and + and specification of absolute zone numbers.
Changed In Version 16.85.0: cutsurf for link files and generators is processed by
ttycomChanged In Version 17.0.2: Zone specification was brought in line with other functions. Allow “plain” cutsurf command without ZSURF to cut just one zone. Proviosly positive values of ZSURF specified the number of zones to be truncated and negative numbers an absolute zone numer; float values were not allowed.
Warning
The change in zone specification introduced with 17.00.02 requires to use “negative zone mumer” where previously a positive number was provided. On the positive side, one can just specity the number of the last zone to keep on the grid as parameter - something that happened often in practice.
Todo
add cutting by density, radius, velocity, temperature, or spacing criterium.
decayni
Convert all APPROX
ni56tofe54in such a way as to conserve mass, but with no energy generation.
name
parameters
decayni
det
Simulate the passage of a detonation wave.
name
parameters
detJDET0 JDET1 ENDET
det 1 30 7.867E+17Same as edep but also change detonated zones to
ni56.Warning
This command should be used only for zones using the APPROX network, and is normally used in conjunction with setting timex0 (p 38) to the current problem time, time (p 2), so that the decay energy from this “newly formed”
is appropriately deposited in the star (see timex0 (p 38)).
edep
Add specific energy to specified zones.
name
parameters
edepJDET0 [ JDET1 ] ENDET
edep 0. .02 1.d17JDET0
Single zone or lower bound of range of zones to be edited.
JDET1
Upper bound zone to be edited.
ENDET
specific energy to add to zones (
erg/g)Add ENDET
erg/gto the specific energies of the specified zones range, inclusive.Processing of zone specification is done similar to the <j> command if only JDET0 is supplied, and similar to the sumb command if both both JDET0 and JDET1 are supplied.
dump
Add dump variable
DUMPVARto the list of variables to be dumped to the qq post-processor dump file or change its dump parameters if it is already in the dump list.
name
parameters
dumpDUMPVAR RATZDUMP RATIODEZ RATIOADZ
dump convect .l -1. 0.
DUMPVARmay be any zonal edit variable, and in addition it may take the values:
value
result
parm
to dump the values of the changeable (‘p’) parameters
qparm
to dump the values of the edit (‘q’) parameters
RATZDUMP
the maximum allowed fractional change between dumps of the specified zonal
RATIODEZ
the minimum fractional change of this zonal dump variable allowed between two adjacent dump grid points before the dump grid for the variable is dezoned
RATIOADZ
the maximum fractional change of this zonal dump variable allowed between two adjacent dump grid points before the dump grid for the variable is adzoned
The associated dump parameters must be given for each variable. In the case of parm and qparm the values of RATIOADZ and RATIODEZ are ignored but dummy values must still be given.
Note
Note that the dump command for new variables is usually given in the problem generator file.
Note
This command may be useful in generators
Deprecated Since Version >15.0.0.
Other entry:
Useful Input Cards
datapath
Set or enquire path to data files.
name
parameters
datapath[ PATH | clear ]
datapath /home/alex/kepler/local_data/PATH
path to data files.
clear
reset the data path.
Set the data path if PATH is specified. Delete the content of
datapathof “clear” is specifies. Display the current data path otherwise.The
datapathvariable is where KEPLER looks for data files if they cannot be found in the local directory.If the environment variable
KEPLER_DATAis set, KEPLER will also look in the path specified in the variable for data file if they cannot be found in the local directory or the directory specified indatapath(if set). This allows for a machine-dependent setting of the data path and is probably the better way in most cases when general/global files are to be used. The use of datapath allows. however, to give the location of specialized files (maybe as relative path). In both cases,datapathandKEPLER_DATA, the character “~” (tilde) is replaced by the value of the system variable “HOME”, allowing for machine-independent specification of paths.Note
It is more portable to use environment variables or keep the data files or links to them in the local directory.
New In Version >15.0.0.
Todo
Check whether this is not already in
ttycomOther entry:
Useful Input Cards
genburn
name
parameters
genburnNAMEBG
genburn sol160bgNAMEBG
name of generator file to read
Read BURN generator, NAMEBG, and begin BURN co-processing.
Note
This command is usually given in the problem generator file.
link
Read and execute the LINK file.
name
parameters
linknamelink
link linkwlsnRead and execute the LINK file named NAMELINK. The link file may contain the information needed to link the results of specialized core collapse calculations or parameterized models back to KEPLER in order to follow the subsequent explosion and nuclear processing. See the
linksubroutine.Changed In Version 16.85.0: The link file may contain any TTY command and any command that used to be in the LINK files is now accesssible, though not always useful, as interactive command.
lista
List all aliases, including those not yet defined (which are denoted by “null”). ‘.
name
parameters
lista
mix
Simulate mixing due to RT instabilities.
name
parameters
mix[ NZMIN NZMAX ] DLTMASS [ TERMINATE ]
mix 293 507 0.5 0NZMIN NZMAX
Zone range (inclusive) in which to mix. Processing of the zone specifications is done the same way as for the sumb command. If omitted, all zones are mixed.
DLTMASS
Mass of mixing window (
Msun)TERMINATE
Terminate KEPLER if mixing fails and TERMINATE is
1but continue otherwise, which can be dangerous and will not produce useful results in general. Default value is1Mix composition outwards starting with zone NZMIN and ending with zone NZMAX in mass increments of DLTMASS (
Msun). Reset the equation of state in mixed zones. Used for light-curve calculations to simulate Rayleigh-Taylor mixing.Changed In Version 17.0.2: Generalized zone range specification.
Changed In Version 17.6.1: Default value for TERMINATE changed from
0to1.Changed In Version 17.6.2: Make NZMIN and NZMAX optional.
mixdiff
Simulate mixing due to RT instabilities using diffusion approach.
name
parameters
mixdiff[ NZMIN NZMAX ] DLTMASS [ TERMINATE ]
mixdiff 293 507 0.5NZMIN NZMAX
Zone range (inclusive) in which to mix. Processing of the zone specifications is done the same way as for the sumb command. If omitted, all zones are mixed.
DLTMASS
Mass of mixing width. (
Msun)TERMINATE
Terminate KEPLER if mixing fails and TERMINATE is
1but continue otherwise, which can be dangerous and will not produce useful results in general. Default value is1Mix composition using one-step implicit diffusion solver with a DLTMASS
(
Msun) diffusion-like approach with diffusion relative to mass coordinate (diffusion is constant relative to mass coordinate). Mixing is done in the zone range starting with zone NZMIN and ending with zone NZMAX.Reset the equation of state in mixed zones. Used for light-curve calculations to simulate Rayleigh-Taylor mixing.
New In Version 17.6.2.
mixcycle
Perform mixing/diffusion operation using current coefficients.
name
parameters
mixcycle[ IZERO ]
mixcyle 1IZERO
if set to
1the diffusion coefficiients are zeroed after operation. This is also default. Set to0to prevent erasing of diffusion coefficients.If mixcycl (p 433) is
1the new time step dtnew (p 1) is used, otherwise the old time step is used.Note
If mixcycl (p 433) is
0the mixing operation has already been performed at the end of the cycle and the routine returns with an error message.New In Version >16.0.0.
mode
Echos whether KEPLER is in interactive mode or not.
name
parameters
modemodeThis was used for an IDL interface I wrote.
newdumps
Reset all dump-file names and delete all old dump variables.
name
parameters
newdumpsDeprecated Since Version >15.0.0.
newe
Calculate new internal energies from current densities and temperatures.
name
parameters
neweThis is usually wise when changing EOS’s in the middle of a problem via code modifications or changing EOS parameter settings.
Note
Note that total energies are also readjusted so that the resulting “virtual” energy nonconservation is not reflected in the energy edits.
newt
Calculate new temperature current internal energies and densities.
name
parameters
newtThis may be useful when depositing energy to fix EOS issues.
New In Version 17.0.13.
newqname
Reset the names of the expected qq-file and qlib-file to reflect the current problem name.
name
parameters
newqnameDeprecated Since Version >15.0.0.
newstart
Reinitialize the problem by making an edit and restart dump of the current status of the problem, putting out output files, and storing dumps.
name
parameters
newstartWarning
This command is obsolescent and should not be used on UNIX machines without careful checking of the coding involved.
Deprecated Since Version >15.0.0.
novamix
Mixing for nova test scenario.
name
parameters
novamixDELTAM
novamix 1.d8DELTAM
mass over which to mix (
g)Replace “ramp” of core composition in
layer. The core compositon is taken from zone
1and the edge of of the (/
) core is defined by
exceeding
0.0001.New In Version >15.0.0.
resetvnm
setspin
Change total angular momentum of star.
name
parameters
setspinVALUE [ mult | div | w j ]
setspin 3. multVALUE
new value of total angular momentum of star (
erg*sec)mult, div
multiply or divide current rotation rate by VALUE
j
set local specific angular momentum (
cm**2/sec)w
set local specific angular velocity (
rad/sec)Scale total angular momentum,
, of star to the new value VALUE. If mult or div are provided, the new angular momentum is multiplied or divided by VALUE, respectively, instead. If w j are specified, set the local value of angular velocity or specific angular momentum, repectively, to VALUE.
Note
To enforce rigid rotation afterwards, use the solidrot command.
New In Version >15.0.0.
solidrot
Bring the star to solid body rotation.
name
parameters
solidrotsolidrotNew In Version >15.0.0.
store
Set the directory into which ASCII output files and labeled restart dumps will be written to NSDIRECT.
name
parameters
storeNSDIRECT
store lusrneo/weaverls25s2a'NSDIRECT
If NSDIRECT is set to
no-store” (the default), output files will be placed in the current working directory. The name ofNSDIRECTmay be up to48characters long.Deprecated Since Version >15.0.0.
system
Execute the system command
COMMAND-STRING.
name
parameters
system”COMMAND-STRING”
system "cd lusrneo/weaver"COMMAND-STRING
command sting, less than
72characters longNote
COMMAND-STRING must be enclosed in double quotes
Note
The entire system command may not exceed
80characters and may not, itself, be comma-delimited.
unalias
Remove the previously defined alias
NAMEA.
name
parameters
unaliasNAMEA | all
unalias tl
NAMEAname of alias to delete
all
remove all aliases, including those defined in the generator
reset
If BURN co-processing is being done, reset the timen array and take a small time step by setting dtimen to dtfrac (p 230)
dtnew (p 1).
name
parameters
reset
resetacc
resetdec
Reset deretion parameters xmdec (q 129) and decmass (q 130) to
0..
name
parameters
resetdecNew In Version 16.85.0.
zerotime
Set the problem time, time (p 2), to
0..
name
parameters
zerotimeAdd the old value of time (p 2) to toffset (p 315). Also reset the timen array and take a small time step as descrived in reset if BURN co-processing is being done.
Link Input File¶
LINK input files allow information derived from other codes (especially detailed core collapse calculations) or from parameterized models to be introduced into KEPLER. Typically this information specifies that a certain mass at the center of the star is to be removed and replaced with a time dependent inner boundary condition whose motion and neutrino emission acts like a “piston” to explode the outer layers of the star.
In current KEPLER all link cards are processed by ttycom the
same way at TYY commands or commands from command files.
KEPLER allows to use link file for any purpose, e.g., as a
collection of standardized commands for specific classes of problems
or projects. It is allowed to nest LINK files, however, there is a
limited recursion level (currently about 8)
A link input file named NAMELINK is read into KEPLER when the
command link NAMELINK, e.g.,:
link linkwlsn
is issued from the terminal, command file, or another link file.
Cards specifically designed for LINK files are listed below.
Link Input Cards¶
cut
Core Cut Card.
name
parameters
cutJCORE
cut 57JCORE
Zone up to which to cut out core. Processing of the zone specifications is done the same way as for the <j> command.
Remove the inner JCORE zones from the center of the star. Add their mass to summ0 (p 61), the boundary condition parameter giving the mass inside the inner boundary of the calculation.
approx
Convert zones to APPROX netwrok.
name
parameters
approx[ JLO [ JHI ] ]
approx 1 9JLOW
lower bound of range of zones to be changed
JHI
upper bound zones to be changed
Change zones between JLOW and JHI to the APPROX network (if not already using it). If JHI is omitted, change all zones to the surface. If neither JLO and JHI is given, change the entire star. Processing of zone specification is done similar to the <j> command if only JLOW is supplied, and similar to the sumb command if both both JLOW and JHI are supplied.
The code assumes that non-APPROX zones are either NSE or ISE zones and repacks the abundance array appropriately to put it into APPROX format. Since the ISE abundance array does not store infomlation on (the usually very small) abundances of ions
h1,he3,c12,n14, and Inon:ne20, these end up being zeroed in going to APPROX. Also, isotopes more neutron rich than(e.g.,
) are stored as
fe52in such a way as to conserve mass (but not Ye – also see the ye command below). This command should not be used (or be rewritten) if the resulting abundance offe52is significant. In its current form, it is intended to be used to transform relatively unneutronized zones containing newly synthesizedand/or
which the APPROX network is able to deal with sensibly. Remember to turn on low-temperature
decay (if desired) by resetting timex0 (p 38), and, if desired, time (p 2).
pist
Show piston data.
name
parameters
pistNew In Version >15.0.0.
pst
Piston Cards.
name
parameters
pst( TIME INNER-RADIUS ) | clear
pst clear pst 0. 1.0072e+7 pst 1.e+10 1.0072e+7Note
At least two required if any are specified.
INNER-RADIUS
radius of the inner boundary of the problem (
cm)TIME
time of piston location (unit:sec)
clear
reset piston data and disable piston
A series of such cards with monotonically increasing values of TIME are used to build up a discrete time history of the inner problem boundary, which the code uses to get intermediate values by interpolation. If the INNER-RADIUS given is 0., this serves as a flag for the code to reset its value to RADIUS0, so that a higher precision value can given. This is sometimes useful in treating compact configurations such as surface layers on neutron stars. The range of times covered must exceed the range of times for which the problem is to be run and at least two piston cards must be specified.
Currently, a maximum of
npistz
300pst cards are allowed.npistzis a FORTRAN parameter set inkepcom.Changed In Version 16.85.0: Piston is handled in
ttycom.Changed In Version 17.0.2: Added clear option.
Note
It used to be the case that:
The code does not remember data from 'PST' cards in any previously read |LINK| decks, but does remember this current 'PST' data in restart dumps.Now all use pst clear to reset piston, otherwise it is always stored.
cut
Cut out the inner ZONE zones.
name
parameters
cutZONE
cut 1.5 cut 12ZONE
Upper zone (inclusive) which is to be removed. Processing of zone specification is done similar to the <j> command.
radius0 (p 60) and summ0 (p 61) are updated accordingly.
Changed In Version 16.85.0: moved from link to
ttycomChanged In Version 17.0.2: Added general evaluation of zone specification.
bounce
Generate piston (pst cards) from analytic formula.
name
parameters
bounceXCUT TMIN RMIN RMAX ALPHA [ cut] [ scut ] [ accel ]
XCUT
Zone for piston. Processing of the zone specifications is done the same way as for the <j> command.
If XCUT is a floating point number, however, it is interpreted as the
value where to locate the piston.
TMIN
Time for infall (
sec) or acceleration multiplier if accel is specified.RMIN
maximum position of piston (
cm)RMAX
maximum (terminal) position of piston (
cm)ALPHA
multiplier on free fall acceleration for outward movement of piston
cut
The innermost XCUT zones are cut away (see cut command).
scut
Interprete XCUT as the entropy (
kb/baryon) value where to locate the piston.accel
TMIN is interpreted as the acceleration for the piston infall instead. The time of bounce then depends on the structure of the star. A typical value for TMIN in this case may eb around
0.25(Thomas Janka, prov. com.).This card generates a piston that moves inward from the outer boundary radius of zone XCUT to the radius RMIN (
cm) in a time TMIN (sec). The radius as a function of time is fit by a parabola with the initial slope being the velocity at the outer boundary of zone XCUT. After TMIN the piston moves outwards with the (negated) free fall velocity from a point at radius RMAX (cm) in a gravitational field that is ALPHA times that of the mass enclosed by the outer boundary of zone XCUT. When the maximum position of the piston is reached, the movement of the piston is stopped.If the piston is generated successfully, tshock (p 343) is set accordingly. This is particularly useful if the accel option is used
New In Version >15.0.0.
Changed In Version 17.0.2: Generalized treatment of zone specification was added.
pulsedit
Write out pulsation edit file needed by Isabelle Baraffe’s code.
name
parameters
pulseditFILENAME
pulseditFILENAME
name for file for edit
This file contains several thermodynamical quantities and hard-to-compute derivatives. If FILENAME is not given, the generic name
NAMEPROB-ncyc (q 4) is used.The current version number is
10302The file has the following format / FORTRAN write statement:
ipvers=10302 write(8,"(A,I6,A,I6,A,1P,D25.17,A,D25.17)") & ' [PULSEDIT] VERSION ',ipvers, & ' at cycle ',ncyc, & ', time=',timesec, & ', total time=',timesec+toffset write(8,2487)jm write(8,2488)(rn(i),i=0,jm) ! R (cm) write(8,2488)(zm(i),i=0,jm) ! Mr (g) write(8,2488)(xln(i),i=0,jm) ! L (erg/s) write(8,2488)(tn(i),i=1,jm) ! T (K) write(8,2488)(dn(i),i=1,jm) ! rho (g/cm2) write(8,2488)(pn(i),i=1,jm) ! P (dyne/cm2) write(8,2488)(xsn(i),i=1,jm) ! eps_tot (erg/(s*g)) write(8,2488)(xkn(i),i=1,jm) ! kappa write(8,2488)(xenbtn(i),i=1,jm) ! cv= (d e_in / d T )_ro write(8,2488)(xcp(i),i=1,jm) ! cp= cv*Gamma1/chiro write(8,2488)(xchid(i),i=1,jm) ! chiro=(d ln P/d ln ro)_T write(8,2488)(xchit(i),i=1,jm) ! chit =(d ln P/d ln T)_P write(8,2488)(xsnd(i),i=1,jm) ! d ln eps_tot/d ln ro write(8,2488)(xsnt(i),i=1,jm) ! d ln eps_tot/d ln T write(8,2488)(xknd(i),i=1,jm) ! d ln kappa/d ln ro write(8,2488)(xknt(i),i=1,jm) ! d ln kappa/d ln T write(8,2488)(xabadd(i),i=1,jm) ! d ln Nabla_ad/d ln ro write(8,2488)(xabadt(i),i=1,jm) ! d ln Nabla_ad/d ln T write(8,2488)(xcpd(i),i=1,jm) ! d ln c_P/d ln ro write(8,2488)(xcpt(i),i=1,jm) ! d ln c_P/d ln T write(8,2488)(xabla(i),i=0,jm-1) ! Nabla write(8,2488)(xabad(i),i=1,jm) ! Nabla_ad write(8,2488)(xxf(i),i=1,jm) ! X (mass fraction of H) write(8,2488)(xlcf(i),i=0,jm-1) ! L_conv/L write(8,2488)(xgesc(i),i=0,jm-1) ! v_conv (convective velocity) write(8,2488)(un(i),i=0,jm) ! velocity at lower zone interface write(8,2488)(1.0D0,i=1,jm) ! f_t (a rotation parameter) write(8,2488)(1.0D0,i=1,jm) ! f_p (a rotation parameter) write(8,2488)(xmweight(i),i=1,jm) ! mu (mean molecular weight) write(8,2488)(angw(i),i=1,jm) ! angular velocity write(8,2488)(xye(i),i=1,jm) ! Y_e (electrons per baryon) write(8,2488)(xenbdn(i),i=1,jm) ! (d e_in / d ro )_T write(8,2488)(xsneut(i),i=1,jm) ! eps_nu (erg/(s*g)) "neutrino loss" write(8,2488)(xsneutbt(i),i=1,jm) ! d ln eps_nu/d ln T write(8,2488)(xsneutbd(i),i=1,jm) ! d ln eps_nu/d ln ro write(8,2488)(xsnuc(i),i=1,jm) ! eps_nuc (erg/(s*g)) "nuclear" write(8,2488)(xsnucbt(i),i=1,jm) ! d ln eps_nuc/d ln T write(8,2488)(xsnucbd(i),i=1,jm) ! d ln eps_nuc/d ln ro write(8,2488)(xsnuw(i),i=1,jm) ! eps_nuw (erg/(s*g)) "weak" nu write(8,2488)(xsnuwbt(i),i=1,jm) ! d ln eps_nuw/d ln T write(8,2488)(xsnuwbd(i),i=1,jm) ! d ln eps_nuw/d ln ro write(8,2488)(xsnubps(i),i=1,jm) ! eps_nup (erg/(s*g)) "thermal" nu write(8,2488)(xsnubpsbt(i),i=1,jm)! d ln eps_nup/d ln T write(8,2488)(xsnubpsbd(i),i=1,jm)! d ln eps_nup/d ln ro write(8,2488)(stot(i),i=1,jm) ! stotNew In Version >15.0.0.
pulsednr
Write out pulsation edit file needed by Jeremiah Murphey’s code.
name
parameters
pulsednrFILENAME
pulsednrFILENAME
name for file for edit
This file contains several thermodynamical quantities and hard-to-compute derivatives. If FILENAME is not given, the generic name
NAMEPROB=ncyc (q 4) is used.See subroutine
pulsednrfor detailsThe file has the following format / FORTRAN write statement:
write (8,120) (titl(i),i=1,3),timesec write (8,100) irp1,xlum,totm,teff,radius,xlum0 write (8,110) 1,0,0.0D0,0.0D0,xlum,xlum0,0.1298D0 write (8,150) xrn0,(rn(i),i=iball,ir) write (8,150) xtn0,(tn(i),i=1+iball,ir) write (8,150) xvn0,(xvn(i),i=1+iball,ir) write (8,150) xcv0,(xenbtn(i),i=1+iball,ir) write (8,150) xknd0,(xknd(i),i=1+iball,ir) write (8,150) xknt0,(xknt(i),i=1+iball,ir) write (8,150) xm0,(xm(i),i=1+iball,ir) write (8,150) xkn0,(xkn(i),i=1+iball,ir) write (8,150) xdm0,(xdm(i),i=1+iball,irp1) write (8,150) xgm0,(xgm(i),i=1+iball,irp1) write (8,150) xpn0,(pn(i),i=1+iball,ir) write (8,150) xgamma10,(xgamma1(i),i=1+iball,ir) write (8,150) xgam3m10,(xgam3m1(i),i=1+iball,ir) write (8,150) xlrf0,xlrf(1),(xlrf(i),i=1+iball,ir) write (8,150) xsn0,(xsn(i),i=1+iball,ir) write (8,150) xsnt0,(xsnt(i),i=1+iball,ir) write (8,150) xsnv0,(xsnv(i),i=1+iball,ir) write (8,150) 0.0D0,xqb0,(xqb(i),i=1+iball,irm1),xp0New In Version >15.0.0.
nflux
Neutrino Flux Card.
name
parameters
nfluxTBOUNCE FLUXNU0 A0 CHI0 Al CHI A2 CHI2
nflux 0.21569 9.e+24 2.5e-8 8.0e+7 0.25e-8 8.0e+8 0.4e-8 2.2e+9 (typical) nflux 0.223 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. 0. (no flux)TBOUNCE
bounce time (
sec)FLUXNU0
base flux (
cc/sec**2)A0, Al, A2
amplitudes (
1/cm)CHI0, CHI1, CHI2
time equivalents (
1/cm)This card contains the fitting coefficients for the “reduced” neutrino momentum flux,
, in the form:
and
where we use
value
result
TBOUNCE (
sec)
FLUXNU0 (
cc/sec**2)
resulting reduced local flux
FLUXNU(cc/sec**2)
CHI0 (
cm)
CHI1 (
cm)
CHI2 (
cm)
A0 (
1/cm)
A1 (
1/cm)
A2 (
1/cm)
speed of light (
cm/sec)
current problem time, time (p 2), (
sec)
local radius (
cm)
local distance/time offset
CHI(cm)Note
Note the positive coefficient of A2 in this fit.
Basically, this fit represents the neutrinos as a wave that propagates outward from the inner boundary without significant attenuation. In a typical case, such as that given in the example, this wave turns on exponentially near retarded time CHI0, peaks about retarded time CHI1, and decays away exponentially near retarded time CHI2. The acceleration of the matter due to scattering with this neutrino wave is then given by (
cm**2/sec)
where
is the average atomic weight. This scattering is currently assumed to be elastic, and no thennal energy is deposited. Typically
is derived from edits of neutrino-induced acceleration in the inner mantle zones of detailed core collapse calculations, such as that of Wilson and coworkers. (See
7/25n8KEPLER notes.)
ye
cards for ISE initialization.
name
parameters
ye( ARBITRARY INTERIOR-MASS YEQ0 ) | clear
ye clear ye 1 0. 0.48 ye 2 2. 0.50Note
At least two are required if any are given.
ARBITRARY
arbitrary, but required, value that is generally used to number the ye card
INTERIOR-MASS
interior mass coordinate (
Msun) for thispoint
YEQ0
value of
to be used to initialize new ISE zones at this mass coordinate (
mol/g)clear
reset
initialization data and disable initialization
A series of such cards with monotonically increasing values of INTERIOR-MASS are used to build up a discrete representation of the post-oxygen burning Ye profile, which the code uses to get intennediate values by linear interpolation (see subroutine
sdot). Out of the range of mass coordinates specified by such a set of ye cards, the code uses the minimum of the current (APPROX-generated) value ofand yemax (p 323)) in order to initialize a new ISE zone.
Changed In Version 16.85.0: ye is handled in
ttycom.Changed In Version 17.0.2: Fixed initialization and added clear option.
Note
It used to be the case that:
The code does not remember data from "ye" cards in any previously read |LINK| decks, but does remember this current "ye" data in restart dumps.Now use ye clear to reset
initialization, otherwise it is always stored.
killye
zero
name
parameters
zeroreset all relevant parameter as is stating a fresh run.
This is to be used after, e.g., some initial relaxation step.
zeroFull implementation is still pending.
New In Version 17.7.3.